在前后端不分离的情况下,Thymeleaf模板引擎与SpringMVC的数据交互记录。
前端使用Thymeleaf模板引擎,前后不分离的数据交互方式。
环境部署
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
|
前端请求页面跳转
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>首页</h1>
<p th:text="${msg}"></p>
<a th:href="@{/user/add}">add</a>
<a th:href="@{/user/update}">update</a>
</body>
</html>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| @Controller
public class MyController {
@RequestMapping("/user/add")
public String add(){
return "user/add";
}
@RequestMapping("/user/update")
public String update(){
return "user/update";
}
@RequestMapping("/user/index")
public String index(){
return "index";
}
}
|
页面跳转成功,请求成功。
前端向后端发送数据(RequestParam)
单个数据进行发送
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Login</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>登录</h1>
<hr>
<form th:action="@{/doLogin}" method="post">
<p>用户名: <input type="text" name="username"></p>
<p>密 码: <input type="password" name="password"></p>
<p><input type="submit"></p>
</form>
</body>
</html>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
@RequestMapping("/doLogin")
public String login(@RequestParam String username, @RequestParam String password){
System.out.println(username);
System.out.println(password);
return "index";
}
|
加不加@RequestParam有什么区别呢?
前端给后端发送数据(PathVariable)
如果使用@PathVariable注解,需要在URL路径中添加变量值,并使用{}括起来。例如:
在前端代码中,我们在表单的th:action属性中使用了路径变量,其中(name=${name}, age=${age})指定了变量值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title>PathVariable示例</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>请输入你的姓名和年龄:</h2>
<form method="post" th:action="@{/submit/{name}/{age}(name=${name}, age=${age})}">
<p>
<label for="name">姓名:</label>
<input type="text" id="name" name="name"/>
</p >
<p>
<label for="age">年龄:</label>
<input type="number" id="age" name="age"/>
</p >
<button type="submit">提交数据</button>
</form>
</body>
</html>
|
当用户填写完信息后,点击提交按钮即可将数据发送给后端。后端使用@PostMapping注解指定了处理该请求的方法,并通过@PathVariable注解获取了URL路径中的变量值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
@RequestMapping("/pathVariable")
public String pathVariable(){
return "pathvariable";
}
@PostMapping("/submit/{name}/{age}")
public String submitData(@PathVariable("name") String name, @PathVariable("age") int age){
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(age);
return "/pathVariable";
}
|
前端给后端发送数据(RequestBody)
@RequestBody注解通常用于处理RESTful API的请求。而Thymeleaf是一个服务器端的模板引擎,其主要目的是生成页面和展示数据。因此,在Thymeleaf中并不需要使用@RequestBody注解。
如果后端Controller中使用了@RequestBody注解来处理请求,那么在前端页面中就需要使用AJAX等方式异步提交数据,并且在成功响应后更新页面数据。
这里给出一个示例代码,假设后端Controller代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| @RestController
public class UserController {
@PostMapping("/users")
public User addUser(@RequestBody User user) {
return user;
}
}
|
在前端页面中可以使用jQuery的AJAX方法来异步提交表单数据,并且在响应成功后更新页面数据:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title>添加用户</title>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/jquery/3.2.1/jquery.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>添加用户</h1>
<form id="user-form">
<div>
<label for="name">姓名:</label>
<input type="text" id="name" name="name"/>
</div>
<div>
<label for="age">年龄:</label>
<input type="number" id="age" name="age"/>
</div>
<button type="submit">添加</button>
</form>
<table id="user-list">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>姓名</th>
<th>年龄</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr th:each="user : ${users}">
<td th:text="${user.name}"></td>
<td th:text="${user.age}"></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<script>
$(function() {
$('#user-form').submit(function(event) {
event.preventDefault();
var formData = $(this).serialize();
$.ajax({
url: '/users',
type: 'POST',
data: formData,
success: function(user) {
var userHtml = '<tr><td>' + user.name + '</td><td>' + user.age + '</td></tr>';
$('#user-list tbody').append(userHtml);
$('#name').val('');
$('#age').val('');
},
error: function() {
alert('添加用户失败');
}
});
});
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
在这个示例代码中,我们使用了异步的方式提交表单数据,并且在响应成功后更新了页面中的列表数据。注意,我们没有直接使用Thymeleaf模板来展示用户列表,而是使用了AJAX动态更新页面。
后端给前端数据赋值
给首页上的属性赋值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>首页</h1>
属性:
<p th:text="${msg}"></p>
<a th:href="@{/user/add}">add</a>
<a th:href="@{/user/update}">update</a>
</body>
</html>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
@RequestMapping("/index")
public String index(Model model){
model.addAttribute("msg","Hello,World!");
return "index";
}
|

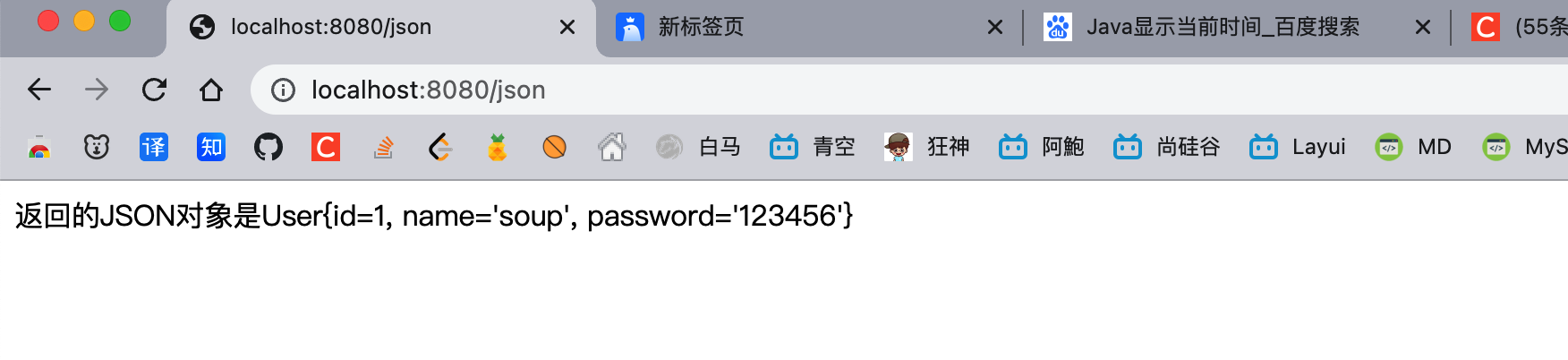
后端给前端发送文字或JSON对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| public class User {
int id;
String name;
String password;
public User(int id, String name, String password) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
@RequestMapping("/json")
@ResponseBody
public String unauthorized(){
User user = new User(1,"soup","123456");
return "返回的JSON对象是"+user;
}
|
MVC常用注解总结
- Controller
- ResponseBody
- RestController
- RequestMapping
- RequestParam
- RequestBody
- PathVariable


